On May 10 2023, Paris played host to a significant event in the world of sustainability. S&P Global's Sustainable1 Summit served as a hub for experts and thought leaders across multiple sectors such as banking, business, and investment management. The gathering was a platform for focused dialogues on urgent sustainability matters. Held at the historic Pavillon Dauphine Saint Clair, a structure originally built for the Universal Exhibition in 1878, the event aligned itself perfectly with its subject matter.
In terms of participants, the summit was a diverse cross-section of academia, industry veterans, and innovators, each sharing their unique insights into the future of sustainability. Key themes of the event centred on biodiversity, climate risk, energy transition, net zero targets, and the inevitable trade-offs on the path to sustainability. A common thread tying these sessions together was the emphasis on a holistic approach, highlighting the interconnected nature of different sustainability factors and the dangers of viewing them in isolation.
S&P Global's Climate Credit Models
In tandem with the summit's various discussions, attendees had the opportunity to delve into S&P Global's offerings in climate data and climate change credit risk modelling. The ever-increasing impact of climate change has driven a demand for models capable of capturing climate-related risks and converting them into measurable financial impacts. Two such models from S&P Global, namely Climate Credit Analytics (CCA) and Climate RiskGauge (CRG), were the focus of these discussions. We present here two, complementary, models for climate change credit risk analysis.
Uncertainty about future outcomes, especially in the horizons considered by climate change analysis, is tackled via scenario analysis. To tackle uncertainty about model selection and performance we use multiple complementary models, two of which we present here. This allows us to explore how, different assumptions and modelling approaches can impact outcomes. CCA provides in-depth analysis, especially when assessing large exposures towards individual counterparties operating in carbon-intensive sectors, when firm-level and sector-specific information are available and become critical to perform a detailed analysis. CRG offers a more portfolio-oriented view and much faster run times, making it better suited for scoring of large number of companies at once, across all sectors, within a consistent framework, especially when companies do not report detailed financials.
Climate Credit Analytics
This robust tool, developed in partnership with Oliver Wyman[1], translates potential climate scenarios into credit risk metrics, aiding users in understanding the effects of different climate scenarios on their portfolios and individual counterparties. This tool is especially useful in benchmarking and scenario analysis, allowing businesses to prepare for a range of potential futures.
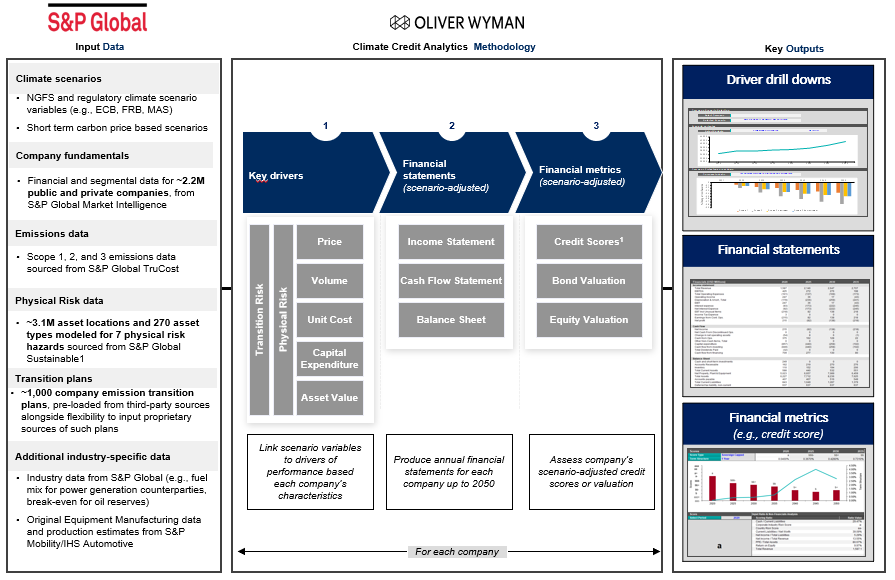
Source: S&P Global Market Intelligence. For illustrative purposes only.
Key Features
- Climate Scenarios: This feature allows for the evaluation of possible credit risk metrics across multiple climate scenarios, providing insights into how varying climate outcomes could influence credit risks. CCA incorporates The Network for Greening the Financial System (NGFS) and regulatory (ECB, FRB, MAS, etc.) variables and scenarios and allows for customized scenarios.
- Company Financials: This feature aids in the examination of the influence of climate change on the credit risk of individual counterparts, enabling informed decisions regarding credit exposure. CCA accesses financials and segment-level data for over 2mn public and private companies, from S&P Global Market Intelligence.
- Company Transition Plans: Company emission transition plans, pre-loaded from third-party sources with a flexibility to input plans from one’s own sources.
- Transition and Physical Risk Data: Scope 1, 2, and 3 emissions data sourced from S&P Global TruCost and c. 3.1M asset locations sourced from S&P Global Sustainable1 allowing efficient and granular estimation of climate risks.
- Additional industry-specific data: Industry data from S&P Global (e.g., fuel mix for power generation counterparties, automotive industry estimates from S&P Global Mobility, Oil reserves data from S&P Global Commodity Insights, etc.)
- High Granularity: This feature offers meticulous insights into specific zones of climate risk, enabling the formation of precise risk management strategies.
- Sector-Specific Insights: This tool delivers insights tailored to various industries, acknowledging that climate change's impact differs substantially across sectors and considers Paris emission reduction goals.
- Probabilistic View: This aspect of the model presents an array of potential outcomes, providing a layered understanding of possible future scenarios.
- Frequent Updates: CCA is regularly updated, ensuring that users consistently have access to the most current climate risk data.
- Geographic Risk Analysis: The model enables the study of climate risks pertinent to specific regions or countries, beneficial for businesses with operations or investments in diverse geographical locations.
- Climate Risk Scores: CCA provides credit scores[2] that encapsulate the degree of climate risk, assisting businesses in grasping the potential severity of impacts.
Climate RiskGauge
This innovative model from S&P Global offers a probabilistic view of how climate risk can influence many companies’ financial performance and creditworthiness, providing a portfolio-level and granular perspective. This tool enables businesses to stay current with the fast-paced evolution of climate risk.
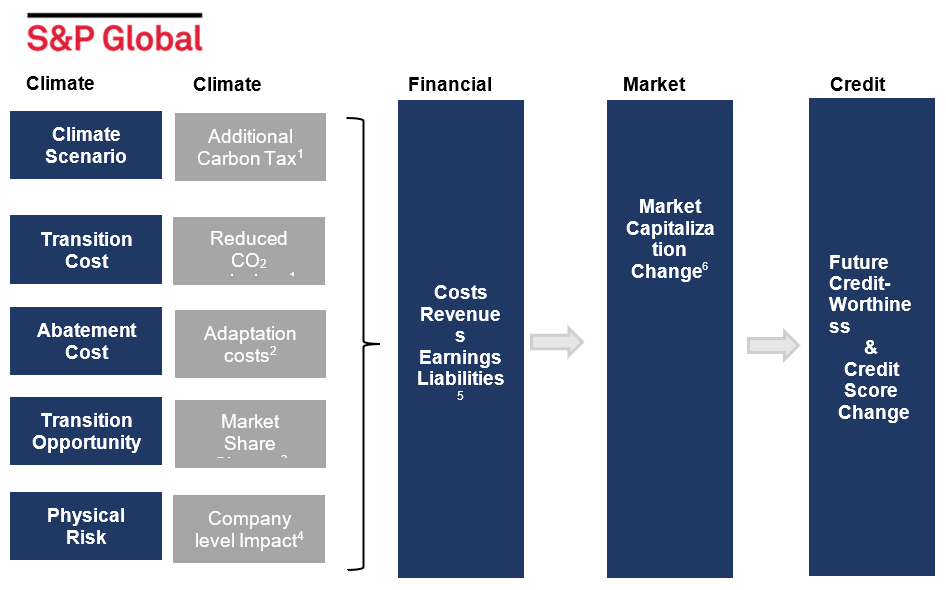
Source: S&P Global Market Intelligence. For illustrative purposes only.
Notes:
- Applied to Scope 1 and 2 emissions. Includes forecasted CO2 reduction.
- Depends on oil price and long-term interest rate.
- Based on proxies for company investments and “firepower” and “consumer awareness”.
- Financial impact function.
- Increase can be switched on/off.
- Assuming “Valuation multiple” remains constant.
Key Features
- Climate Scenarios: CRG represents a global overlay for all public and private firms, with International Energy Association (IEA), Network for Greening the Financial System (NGFS v2.2) or user-defined transition scenarios, leveraging carbon earnings at risk.
- Physical risk: The tool includes Sustainable1’s information on more than 3 million physical assets’ geographical locations, with financial impact aggregated at company level from 7 physical hazards, modelled for various climate scenarios. These scenarios are harmonized with those from NGFS. The overall physical risk impact includes both implications at GDP and company-level.
- Projections of Scope 1 & 2 emissions: the tool generates projections of Scope 1 and Scope 2 green-house gas (GHG) emissions, to support TaskForce for Climate-Related Disclosures (TCFD) reporting.
- Probabilistic View: This aspect of the model presents an array of potential outcomes, providing a layered understanding of possible future scenarios.
- Company-Specific Insights: Able to differentiate by size for companies that can capture market opportunities better – for oil and gas industry in particular.
- Frequent Updates: CRG is regularly updated, ensuring that users consistently have access to the most current climate risk data.
- Geographic Risk Analysis: The model enables the study of climate risks pertinent to specific regions or countries, beneficial for businesses with operations or investments in diverse geographical locations.
- Climate Risk Scores: CRG provides credit scores that encapsulate the degree of climate risk, assisting businesses in grasping the potential severity of impacts.
- Sensitivity Analysis: This feature empowers businesses to scrutinize how alterations in certain variables or assumptions could influence their climate risk, aiding in the creation of sturdy risk management strategies.
- Paris goal tracking & alignment: The tool considers the differential impact of climate change risk (transition and physical) on different industrial (GICS) sectors and considers Paris emission reduction goals.
Conclusion
Recently S&P Global Market Intelligence, was awarded the 2023 “Most Innovative Regulatory Solution for Climate Risk” for their work on the Climate Credit Analytics model (CCA)[3]. This recognition was conferred during the North American Financial Information Summit in New York, earlier this year. Similar sentiment echoes in the feedback we receive from our clients, including global systemically important banks and other large financial institutions.
As we move towards a greener future, comprehending climate risk and its potential impact on creditworthiness becomes increasingly critical. S&P Global's CCA and CRG models equip businesses with robust, up-to-date tools to navigate this intricate field. By using these models, businesses can make more informed decisions, mitigate risk, and identify opportunities in our evolving climate landscape.
[1] Oliver Wyman is a global management consulting firm and is not an affiliate of S&P Global, or any of its divisions.
[2] Lowercase nomenclature is used to differentiate S&P Global Market Intelligence credit scores from the credit ratings issued by S&P Global Ratings.
[3] IMD & IRD Awards 2023: Most innovative regulatory solution (climate risk)—S&P Global Market Intelligence, WatersTechnology, As of June 2023. https://www.waterstechnology.com/awards-rankings/7950924/imd-ird-awards-2023-most-innovative-regulatory-solution-climate-risk-sp-global-market-intelligence.



