Return on equity policy for electric utilities, transmission planning and reliability, and the implications of federal climate and energy legislation are among the key issues on the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission's policy agenda in the coming months as the commission also awaits U.S. Senate action on FERC Chairman Richard Glick's nomination to a new five-year term.
While Glick awaits a hearing on his nomination before a Senate committee, he responded to a June 17 Congressional request seeking information on steps the commission was taking to prevent potential summer power disruptions and maintain grid reliability: "FERC taking slew of steps to boost grid reliability, Glick tells lawmakers."

ROE policy for electric utilities is among the top issues on FERC's fall agenda in the wake of the recent opinion by the U.S. Court of Appeals for the D.C. Circuit vacating and remanding FERC's orders in the Midcontinent ISO cases. The future direction of the commission's policy will likely have significant implications for recently concluded and pending cases featuring contested ROEs.
Other major issues on the commission's agenda include transmission planning and grid reliability, certifying and assessing climate impacts of new gas pipeline facilities, and preparations for the next meeting of the Joint Federal-State Task Force on Electric Transmission in November.
Currently pending cases at FERC highlight ROEs incorporated into transmission and wholesale sales rates, the proposed acquisition by a utility in Michigan of a large gas-fired plant to replace retiring coal generation resources, and a $918 million new gas pipeline project in Virginia.

Among prominent proceedings at the commission, FERC is reviewing and processing nearly 200 filings commenting on the commission's first comprehensive transmission planning rulemaking in more than a decade: "Transmission owners, consumers spar over changes to FERC's competition rules" and "State regulators, DOE weigh in on FERC's transmission planning proposal."
In other proceedings at FERC, noteworthy developments during the last month in the electric power sector included a transmission rate filing submitted by PPL Corp. subsidiary PPL Electric Utilities Corp. to transition the company's formula rate to a calendar year and implement a blended ROE prescribed in a 2021 settlement of a complaint filed by the utility's industrial customers.
In a wholesale sales case, FERC issued an order establishing hearing and settlement judge procedures on a rate increase proposed by Southern Co. subsidiary Mississippi Power Co. incorporating a 9.875% ROE based on the company's ROE in a state retail rate case.
In addition, Consumers Energy Co. asked FERC to approve the company's acquisition of a large gas-fired generating plant in Michigan to help meet the company's goal of ending the use of coal as a fuel source by 2025.
In the natural gas sector, TC Energy Corp. subsidiary Columbia Gas Transmission LLC submitted an application to build the nearly $1 billion Virginia Reliability Project to provide "much needed" natural gas supply to residential, commercial and industrial consumers in southeast Virginia.
A more detailed discussion of these developments that Regulatory Research Associates is following is provided below.
The commission
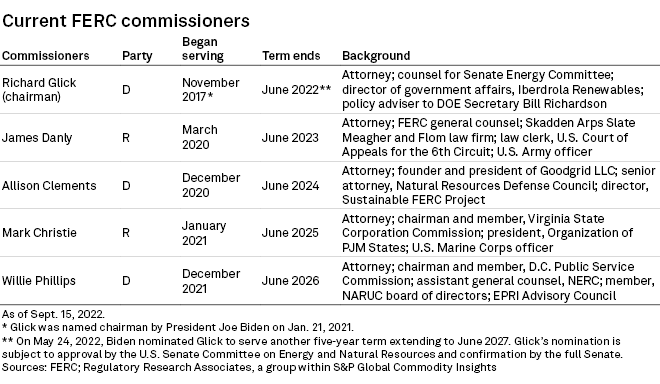
U.S. President Joe Biden's nomination of Glick in May to serve another five-year term at the commission awaits action in the U.S. Senate.
Glick, a Democrat, was serving a term that expired June 30. If his renomination is approved by the Senate Energy and Natural Resources Committee and confirmed by the full Senate, Glick would serve a new five-year term expiring June 30, 2027.
The other FERC commissioners and the dates their terms expire are James Danly, a Republican, June 2023; Allison Clements, a Democrat, June 2024; Mark Christie, a Republican, June 2025; and Willie Phillips, a Democrat, June 2026.
Formula transmission rate ROE — PPL Electric Utilities
On Aug. 25, PPL Electric Utilities filed proposed revisions to its transmission formula rate and implementation protocols to transition to a calendar year rate year from the company's current midyear rate year from June 1 to May 31.
PPL's proposed tariff revisions were filed pursuant to a settlement FERC approved Nov. 5, 2021, that resolved a complaint filed by a group of the utility's industrial customers and revised the base return on equity incorporated into PPL's formula rate from 11.18% to 9.90% effective May 21, 2020, to May 31, 2022, from 9.90% to 9.95% from June 1, 2022, to May 31, 2023, and from 9.95% to 10.00% beginning June 1, 2023.
As part of the 2021 settlement, PPL agreed "to modify the rate year used to populate the formula rate template from the current June 1 to May 31 rate year period to reflect a projected rate year based on the calendar year of January 1 to December 31." The settlement also required that a blended ROE be used for the rate year if the change from a midyear to a calendar year rate year occurred in a year when the base ROE changed June 1 in accordance with the settlement. PPL noted that this is the case in the company's instant filing because the company's base ROE increases from 9.90% to 9.95% on June 1, 2022, and from 9.95% to 10.00% on June 1, 2023.
PPL said the company plans to implement the annual formula rate update process and post a populated rate template on or before Oct. 31, with rates to be effective in the calendar year Jan. 1, 2023, through Dec. 31, 2023.
The 2021 settlement of the complaint did not affect any incentive ROE adders enjoyed by PPL, including a 50-basis-point ROE adder authorized by FERC for the company's participation in the PJM Interconnection LLC.
FERC also approved a 125-basis-point ROE incentive adder in 2008 for PPL's investment in the $1.35 billion Susquehanna-Roseland transmission line project developed jointly with Public Service Enterprise Group Inc. subsidiary Public Service Electric and Gas Co. FERC also authorized PPL and Public Service Electric and Gas to include 100% of construction work in progress for the project in rate base, and the transmission line was placed in service in 2015.
Wholesale sales tariff and ROE — Mississippi Power Co.
On Sept. 13, FERC issued an order accepting and suspending proposed tariff revisions filed by Mississippi Power Co., or MPC, and established hearing and settlement judge procedures to consider the company's proposal to increase wholesale rates charged to municipal and rural association customers by $23 million.
MPC said the rate increase is necessitated by "increases in the cost of doing business since its last approved rate change in 2021, combined with the full amortization of certain specific deferred income tax regulatory liabilities associated with the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act."
MPC requested that FERC approve a 9.875% ROE based upon the ROE approved by the Mississippi Public Service Commission in the utility's performance evaluation plan, a formula-based alternative regulation plan that provides for annual rate adjustments and reflects timely recognition of new investments and fluctuations in operating costs. See the Mississippi state regulatory review for additional details.
MPC said the proposed ROE of 9.875% was calculated by an independent consultant for use in MPC's retail rate case for 2022. MPC explained that the ROE was determined by averaging two costs of equity methods: the discounted cash flow, or DCF, indicating a 9.779% ROE and a regression analysis indicating a 9.721% ROE. MPC stated that the average of these two methods, plus a 0.125% issuance cost adjustment, resulted in a 9.875% total ROE.
MPC also said FERC has stated that the commission has discretion to consider ROE methodologies on a case-by-case basis and has never foreclosed the proposed use of a state-approved ROE covering all integrated retail power supply operations as a proxy for vertically integrated, wholesale bundled generation and transmission cost of service.
On Aug. 5, Cooperative Energy filed a protest of MPC's proposed tariff revisions. Under the tariff, MPC provides wholesale requirements service to various electric power associations, including Cooperative Energy, a generation and transmission cooperative.
With respect to MPC's requested ROE, Cooperative Energy's protest argued that FERC "has made clear that it finds 'state-authorized and commission-authorized ROEs are conceptually distinct and do not necessarily need to be aligned' and that 'it is not legally required to base its jurisdictional transmission ROE determinations on the ROEs determined by state utility commissions.'"
Cooperative Energy added that MPC "inappropriately utilizes a two-model approach to calculate ROE (the DCF model and a regression analysis) relied on by the [Mississippi Public Service Commission] rather than the three-model approach that [FERC] relies on (DCF model, the Capital Asset Pricing Model and the Risk Premium method)."
FERC's Sept. 13 order establishing hearing and settlement judge procedures determined that MPC's filing "raises issues of material fact that cannot be resolved based on the record before us and that are more appropriately addressed in the hearing and settlement judge procedures." FERC specifically noted that material issues of fact to be addressed include MPC's development of the power sales cost of service and the ROE methodology used to calculate the company's cost of equity.
Utility gas plant acquisition — Consumers Energy
On Aug. 18, Consumers Energy Co. filed an application seeking FERC's approval for the company's proposed acquisition of the New Covert Generating Facility, a 1,176-MW natural gas-fired combined-cycle generating facility in Covert, Mich.
Consumers Energy said the proposed acquisition of the facility is part of a comprehensive 20-year Clean Energy Plan that provides for the retirement of all of the company's coal generation resources by 2025. Over the 20 years of the Clean Energy Plan, Consumers Energy said will transform its generation fleet by ending the use of coal as a fuel source by 2025 and adding approximately 8,000 MW of solar generating capacity.
Consumers Energy said it plans to include the facility in the Midcontinent ISO planning reserve auction for 2023. Consumers Energy asserted that including the facility in MISO's 2023 auction will "add much-needed capacity to the MISO market particularly to [a local zone] where the company's service territory is located."
Consumers Energy noted that the facility is within the MISO footprint but is interconnected to the transmission system operated by the PJM Interconnection. As a condition to the closing of the proposed acquisition, the company said the facility will interconnect to the MISO transmission system and participate in MISO markets.
Consumers Energy said that in accordance with FERC's merger policy, the proposed acquisition "would not have an adverse effect on competition, rates or regulation and would not result in cross-subsidization of a non-utility associate company or the pledge or encumbrance of utility assets for the benefit of an associate company."
New gas pipeline project — Columbia Gas Transmission
On Aug. 24, Columbia Gas Transmission filed an application seeking FERC's approval for the $918 million Virginia Reliability Project to be located in southeast Virginia.
The proposed expansion project consists of replacing approximately 49 miles of existing 12-inch diameter pipeline with new 24-inch diameter pipeline located mostly within Columbia's existing right of way as well as certain modifications to existing compressor stations and other infrastructure. The company said the proposed expansion will create 100,000 Dth/d of incremental mainline capacity on Columbia's pipeline system.
Columbia noted that it has executed a binding precedent agreement with Southern Co. subsidiary Virginia Natural Gas Inc., an unaffiliated local distribution company, for 100% of the project's expansion capacity beginning Nov. 1, 2025, for a 20-year term. Columbia also said the project will enable the company to replace and upgrade existing pipeline facilities with "new, more modern pipeline facilities to provide continued safe and reliable natural gas transportation service to existing customers on its pipeline system."
Columbia said it will provide service to Virginia Natural Gas at negotiated rates in accordance with the negotiated rate authority in Columbia's existing FERC gas tariff and will file the negotiated rate agreement with the commission 30 to 60 days prior to when the negotiated rates are proposed to become effective.
Columbia said it designed the initial tariff rate based on a 12.98% rate of return and cost-of-service factors approved by the commission in the company's last two general rate cases in 1997 and 2021.
Columbia proposed to allocate the costs of the project between the replacement of the existing pipeline and the costs to create the incremental expansion capacity. Columbia noted that the costs associated with the replacement portion of the project, approximately $607 million, have been separated from the cost of the expansion portion of the project. The total cost of the $918 million project includes allowance for funds used during construction.
Columbia said that consistent with FERC policy concerning incremental rates, the company will maintain a separate record of capital costs for the facilities in its books and accounts. In addition, Columbia will maintain separate accounts "for volumes transported, billing determinants, rate components, surcharges, and revenues associated with the negotiated rates in sufficient detail so that they can be identified in any future" [general] rate case.
Regulatory Research Associates is a group within S&P Global Commodity Insights.
This article was published by S&P Global Market Intelligence and not by S&P Global Ratings, which is a separately managed division of S&P Global.



