451 Research is a technology research group within S&P Global Market Intelligence. For more about the group, please refer to the 451 Research overview and contact page.
Generative AI refers to AI models that generate new content. The advent of ChatGPT, launched in November 2022, represented the technology trend pivoting from research to monetized products and services. This report explores highlights from the most recent update of 451 Research's Generative AI Market Monitor & Forecast, a data product that profiles the vendor landscape and is built using revenue models for each vendor active in the market, a bottom-up approach informed by 451 Research's proprietary market intelligence.
For companies to be included in the Generative AI Market Monitor & Forecast, they have to offer a packaged software product, where generative AI capabilities are core to that product's value proposition. The Market Monitor is built to account for general-purpose software — designed to address a range of use cases and customer segments — that sit within the following segments: foundation models, text generators, image generators, code generators, audio generators and structured data generators.

Despite the monetization struggles of many of the trend's most prominent startups, illustrated by Inflection AI's loss of much of its core team to Microsoft Corp., aggregate market revenue is steadily expanding. Organizations have a keen interest in generative AI and see the opportunity as spanning the entire business. When asked where they see generative AI delivering value to their organizations, 45% of respondents to 451 Research's Voice of the Enterprise: AI & Machine Learning, Use Cases 2024 survey indicated process automation. Other popular areas ranged from customer interaction (41%) to employee training (39%). Organizations are already seeing an impact in these areas. Even organizations that lacked formally adopted tools — being in the process of making capabilities available, or merely seeing generative AI products being used on an individual basis without organizational support — saw notable improvements in operational efficiency.

Significant growth, outstripping earlier forecasts
This enthusiasm is rapidly being converted into organizational technology spending, with many businesses and institutions willing to invest in upgrading users to commercial tools. This is in part because early experimentation with public-facing tools suggests they may offer significant impact, and with generative AI tools being so widely used, organizations are keen to ensure those tools can meet privacy, relevancy and risk requirements. On the supply side, the expense of training and serving models has led to startups needing a fast ramp-up in terms of revenue to remain commercially viable, and this has compressed the period between research and productization.
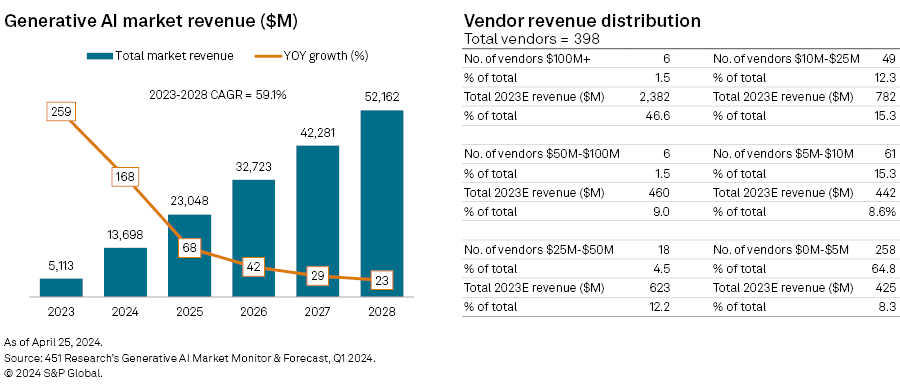
The first edition of the Generative AI Market Monitor, released in June 2023, forecast revenue of $3.7 billion for 2023. Our revised figures, as of the first quarter of 2024, represent a significant uptick, with 2023 aggregate revenue recalculated at $5.1 billion. With a compound annual growth rate of 59% through 2028 and, as illustrated below, particularly pronounced growth figures for the next two years, the generative AI market appears to be growing at an explosive rate. This revision was driven by a number of factors:
– Accelerated enterprise road maps for generative AI: Data privacy concerns with public-access generative AI tools, and the heavy use of these offerings within organizations, have encouraged organizations to invest in rapidly migrating staff to more closely controlled toolsets. An additional upgrade lever for commercial offerings derives from a desire to better tailor generations, or anchor responses more closely to organizational data, to improve their utility in enterprise environments. Under 30% of respondents to 451 Research's VotE: AI & Machine Learning, Use Cases 2024 survey from organizations that have invested in AI had not also invested in generative AI. A plurality of organizations is in the process of making capabilities available, with the desire to rapidly establish an organizationally supported toolset.
– The emergence of new providers: The total number of vendors mentioned in the Market Monitor expanded from 262 to 398. In part, this expansion reflected new startups, some emerging from stealth, but the largest revenue impact came from a cohort of large established technology providers releasing new, monetized generative AI offerings late in 2023. This included a number of Chinese companies, with the first approved generative AI chatbots released to the Chinese public not made available until Aug. 31, 2023, alongside an array of other offerings, ranging from Generative AI by Getty Images to NTT Corp.'s release of its large language model "tsuzumi."
– A trend toward commercialization: Despite the ongoing releases of open-source models, many of the most prominent developers of these models have started to pair these releases alongside tooling or "commercial" models. Stability AI's developer platform and tweaks to model licensing, or Mistral's Small, Large and Embed "optimized commercial models" are illustrative here. The ever-growing cost of training models has put significant pressure on AI project teams to develop commercial propositions that can improve the long-term sustainability of their research. In addition, open-source models have set a foundation for a burgeoning ecosystem of startups offering wraparound tooling for businesses.
AI gaining traction beyond North America
The US continues to represent the largest market for generative AI, with 64% of revenue for 2023 going to AI providers with headquarters in North America. In total, 227 generative AI vendors mapped in the Market Monitor report had headquarters in the US. A contributing factor to this dominance is more mature demand in the region. This is illustrated by the higher proportion of organizations with US headquarters responding to 451 Research's AI & Machine Learning, Use Cases 2024 survey that had generative AI tools adopted and rolled out widely within their organizations than peers in the UK, Germany or France. A strong foundation of academic research and private funding also provides a conducive environment for AI startups. Higher growth rates in Asia-Pacific and Europe, the Middle East and Africa are forecast to gradually erode North America's dominance, with its revenue share falling to 55% by 2028.
Regional constraints in the availability of financial capital, AI accelerators and even access to sufficient electricity, will likely influence the development of generative AI hubs, as will geopolitics. In particular, a divide appears to be emerging between a China-led market and a US-led one, a tension illustrated by G42, with headquarters in Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, divesting its stake in Chinese companies before Microsoft invested $1.5 billion in the AI company. The governments of many countries — including the UK, UAE and South Korea — have expressed a strong desire to build domestic AI companies. This desire and the championing of startups outside of the US, be that Mistral AI in France or Sarvam AI in India, are somewhat mitigating the concentration risks we forecast for the foundation model segment in particular. Language models emerging outside the US can be couched as being more performant for a specific set of languages, but there is also a desire in some countries to use models better aligned with cultural values or contexts. Japan's ruling Liberal Democratic Party released a white paper that raised concerns about how Japan was depicted by popular generative AI models. These factors provide an ongoing dynamic that will likely continue to influence the regional mapping of the 451 Research Market Monitor & Forecast.
Eroding market definitions; comparative sector growth
The generative AI market initially emerged with clusters of specialist providers centered on specific modalities. The vendor space could be easily divided between text, video, audio, image, structured data and code — with the bulk of startups focusing on text following the success of ChatGPT. Many multi-modal models have emerged, where models are trained to receive and output different modalities — being able to generate both text and image, for example. In addition, as many application providers start to explore opportunities to augment or automate various stages in a workflow, there has been an attempt to chain different models together, including those that can generate different formats of output. Expanding the range of models that a technology provider can make available to customers is a commonality across many of the road maps presented to 451 Research analysts. This has contributed to an expansion of vendors outside of text generation as the Market Monitor is updated, as well as the text generator segment being forecast to decline from 24% to 19% of the total market from 2023 to 2028.
Code generators are forecast to see the most pronounced growth rate. This growth reflects both the early demand that popular products (like GitHub Copilot) have seen, and the improving performance of leading models. In particular, 451 Research sees the strict quality assurance processes applied to software development as being well suited to generative AI, guarding against some of the early challenges organizations have faced in applying generative AI in other areas; where incorrect responses could lead to user dissatisfaction, legal challenges or reputational damage, for example. In particular, the model forecasts significant aggregate revenue growth for this segment in 2023 and 2024 — 297% and 208%, respectively.
This article was published by S&P Global Market Intelligence and not by S&P Global Ratings, which is a separately managed division of S&P Global.



