S&P Global Ratings' sustainability insights provide transparency on established and emerging environmental, social, and governance risks and trends—and how they impact economies, companies, and markets.
Data centers are increasingly becoming an integral part of global economic growth and a fundamental societal need. However, growing demand for data centers is not without its drawbacks.
As investors continue allocating capital toward financing data center projects, how increasing infrastructure development and energy demands are balanced today may shape tomorrow's credit and economic landscape.
In this Credit FAQ, S&P Global Ratings' private markets and sustainable finance experts answer questions on the risks and opportunities of data centers as an asset class, alongside assessments of the associated climate and transition risks.
READ MORESustainable finance is about more than funding activities and investments that already foster a greener, low-carbon, and more climate-resilient future in alignment with the Paris Agreement. It's also about financing those that aren't yet compatible to the same degree but do contribute to a reduction of greenhouse gas emissions.
In our inaugural Sustainability FAQ, we answer market participants’ questions on how we view green and transition financing through our coverage and capabilities.
READ MORE >Companies may be underestimating their exposures to physical climate risks if they fail to consider value-chain exposures in their risk analyses. In turn, they may also be underestimating potential operational and financial impacts.
All sectors inherit at least some physical climate risk exposures from their value chains, including those with relatively limited direct risk exposure - but most exposed are those that rely on climate sensitive upstream sectors.
Whether physical climate risks embedded in value chains have material credit impacts depends on many issuer specificities.
Although the volume of clothes produced and sold globally is increasing alongside its environmental impact, the apparel sector's carbon emissions, waste, and pollution risks remain largely unpriced.
At the same time, the financial impact of environmental risks on the sector and our ratings has so far been negligible, reflecting a lack of stringent environmental regulations and little change in consumers' buying behavior.
We believe value- and fast-fashion retailers--whose earnings are mostly led by volumes--could become more exposed to these increasing risks than luxury brands.
The primary credit transmission channels for food safety issues are operational disruption and adaptation, regulation and litigation, and consumer awareness.
Food safety vulnerabilities can occur at all stages of the value chain.
When food safety incidents arise, the negative credit impacts will depend on issuer circumstances and responses, as well as the nature of incidents.
READ MORE >Green bonds will continue to dominate issuance, with transition and sustainability-linked bonds potentially helping to push total sustainable bond issuance to $1 trillion this year.
More than $900 billion of rated outstanding sustainable bonds mature in the next two years and nearly $2.5 trillion before the end of the decade, testing market participants' commitment to climate action and the strength of the sustainable bond market.
Efforts to close the climate finance gap in lower-income countries, a rebound of sustainability-linked issuance, a broader base of transition bond issuers, or expanding issuance in China could be swing factors for 2025 volumes.
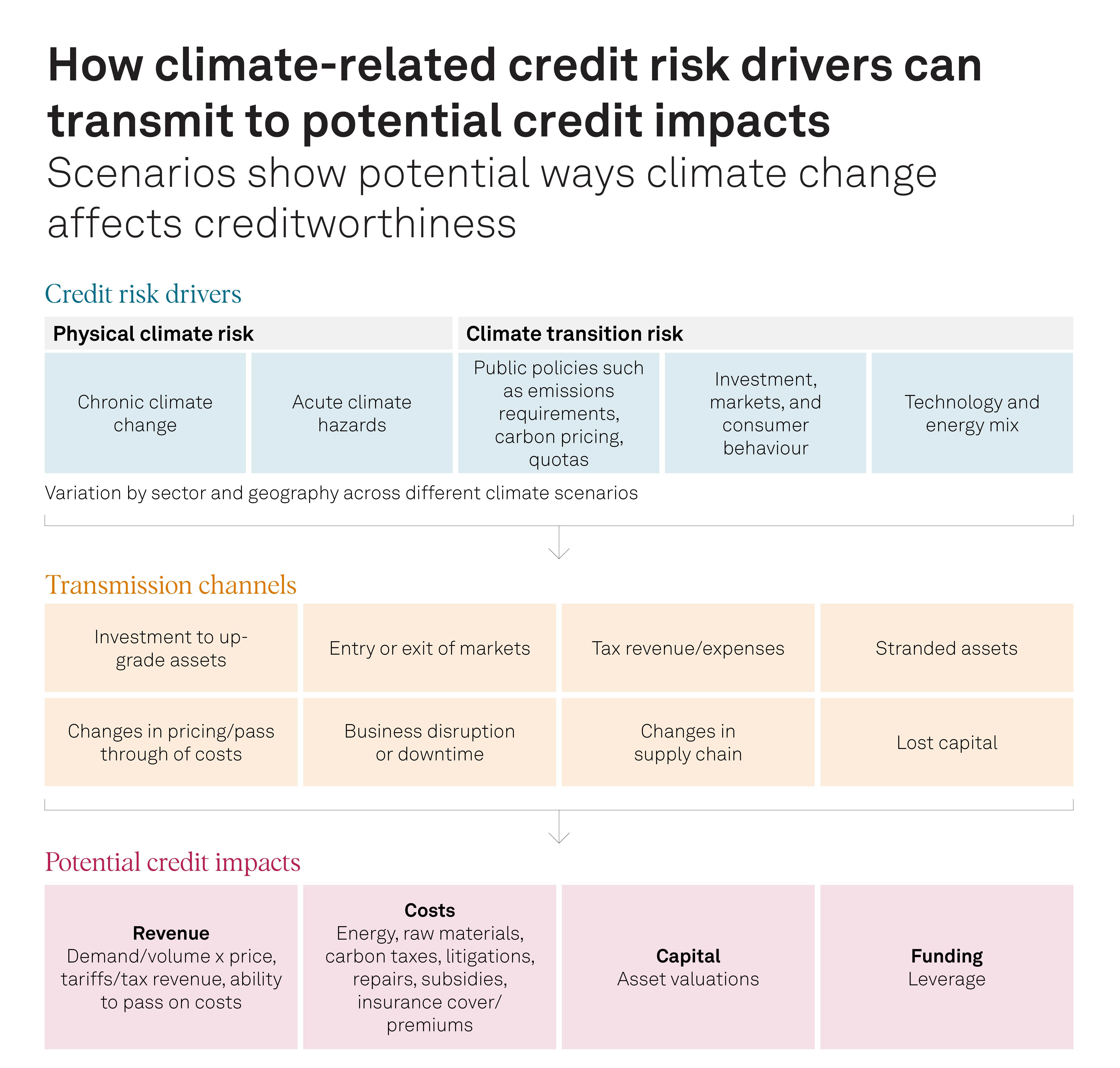
Climate change is a megatrend that can have material impacts on the creditworthiness of issuers and debt instruments.
In our latest white paper, S&P Global Ratings presents plausible long-term scenarios to help illustrate the potential impacts of climate change on credit transmission channels—and ultimately on creditworthiness.
We define three scenarios for climate transition risks, and four for physical climate risks, in line with our five-step process to assess the credit materiality of megatrends. We incorporate takeaways from climate scenario analyses we have conducted, with the aim of providing possible common ground for similar analyses in the future.
ASSESSING HOW MEGATRENDS MAY INFLUENCE CREDIT RATINGS >