The first article in our “When Sovereigns Default” series looked at the need for bondholders to keep a close watch on the credit risk of individual countries around the world given the negative economic impacts we are seeing as a result of COVID-19. The second article presented estimates of loss given default (LGD) for 121 rated countries under a COVID-19 scenario, pinpointing areas of potential concern. LGD is an estimate of the portion of an exposure (bond or loan equivalent) that will likely not be recovered in the event of default, and was calculated using our Sovereign LGD Scorecard. This Scorecard produces estimates of LGD that are point-in-time (PiT), reflecting current economic conditions – an essential approach during a pandemic. The PiT feature captures the fact that default during an economic downturn is typically accompanied with lower recoveries. This third article explains our approach to estimating LGD in more detail.
Sovereign LGD Estimation – A Unique Approach
Our LGD Scorecards were constructed over 17 years ago with the aim of estimating LGD at the exposure level. We believe that LGD should be conditional on explanatory variables and exposure specifics, resulting in more reliable facility- or bond-specific, PiT estimates of loss for any exposure, secured or unsecured. To achieve this, we undertook extensive research in order to identify possible explanatory variables, placing equal emphasis on both qualitative and quantitative factors. We identified six drivers of loss:
- Pre- and post-default quantity and riskiness of cash flow/assets/economic value
- Seniority of exposure (e.g., a senior bond)
- Jurisdiction
- Economic expectations
- Collateral and guarantees/insurance
- Recovery costs and workout policy (restructuring versus disposal)
These factors were further refined for sovereign-specific elements, including post-default expectations of support (e.g., bilateral or multilateral), expectations of post-default economic/political stability, and historical default experience. The final Scorecard inputs – which include a combination of macroeconomic, fiscal, and market indicators – were selected based on the ease of availability of forecast data. Since many credit-sensitive institutions are exposed to a large number of bonds/loans, the LGD approach must be efficient, which is especially important when reporting under IFRS 9. We, therefore, linked input data (e.g., macroeconomic data) to the Sovereign LGD Scorecard using bond ISINs[1] to generate PiT estimates of loss, resulting in robust LGD estimates for large portfolios.
Figure 1:
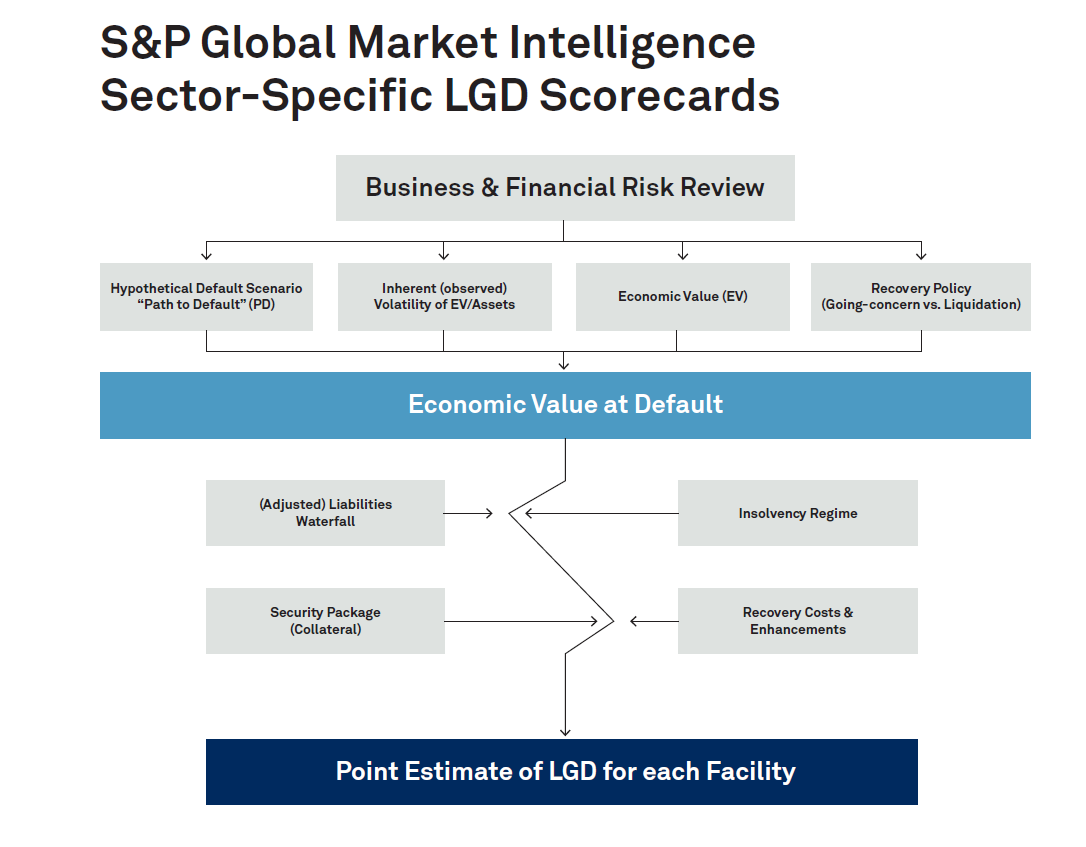
Source: S&P Global Market Intelligence LGD Scorecard Engine, March 12, 2020.
Sovereign LGD Estimation – A Robust Performance
The Sovereign LGD Scorecard was back-tested between 1999-2017 on 172 defaulted bonds. It demonstrated robust performance, forecasting the correct LGD bucket for almost 97 bonds (~60%), while 160 bonds (~99%) were within +/- 1 of the correct bucket. The actual average loss for the sample was 63.8%, while the forecasted average loss was 64.4%.
Figure 2:
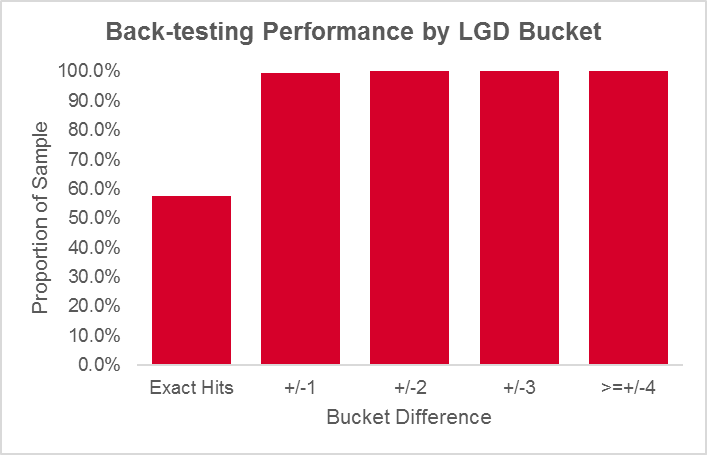
Source: S&P Global Market Intelligence Sovereign LGD Technical Document, December 31, 2019. For illustrative purposes only.
The performance of the LGD Scorecard was also robust across geographic regions, which is important given the global applicability of the Sovereign LGD Scorecard.
Figure 3:
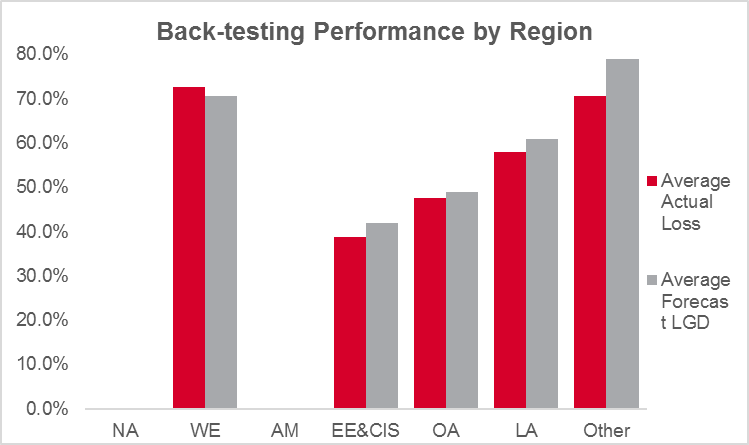
Source: S&P Global Market Intelligence Sovereign LGD Technical Document, December 31, 2019. For illustrative purposes only.
Given the PiT approach used in our Sovereign LGD Scorecard, and its good performance in back-testing exercises, we believe that it is a suitable tool for assessing credit risk in a COVID-19 environment. Our first article in this series showed results for LGD based on forecasts for the same timeframe that were made pre- and post-COVID-19 in order to gauge the impact of the pandemic.
Please click here for more information on our Sovereign LGD Scorecard.



